Top 10 Reasons Generators Fail and How to Prevent Them
Generators are crucial for providing backup power during outages, ensuring the continuity of essential services and operations. However, like all mechanical systems, they can fail. Understanding the common reasons behind generator failures can help develop a preventive maintenance plan and ensure reliability when needed.
Here are the top 10 reasons generators fail and how to prevent these issues:
Table of Contents
Generator Fuel Issues
Stale fuel, especially in generators that sit idle for long periods, loses its combustibility, leading to hard or no starts. Bad fuel, contaminated with water, dirt, microbial growth, or other contaminants, can cause starting problems, poor engine performance, and increased wear on fuel system components. Fuel contamination can also lead to corrosion and damage within the fuel system. Fuel filters help prevent this; however, they can become clogged, restricting fuel flow to the engine.
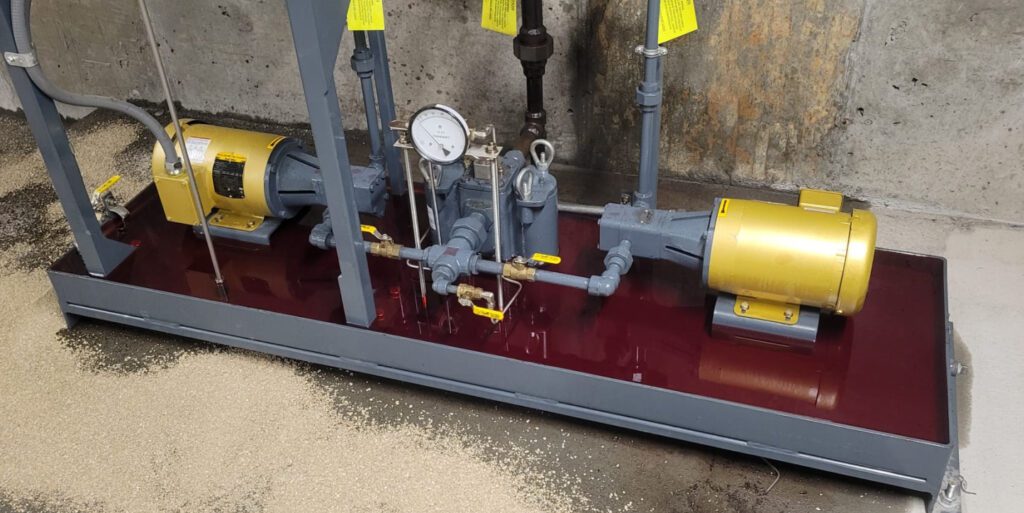

This results in insufficient fuel delivery, causing the generator to run rough, lose power, or stall altogether. Over time, a clogged fuel filter forces the fuel pump to work harder, potentially leading to premature pump failure. Leaks in the fuel lines can cause uneven fuel delivery or air pockets obstructing fuel flow. This leads to hard starts, no starts, sputters, misfires, or the engine to stall. Fuel issues will cause inconsistent performance and reduced power output.
How to prevent generator fuel issues?
- A good preventive maintenance plan includes annual replacement of fuel filters and inspection of the fuel lines
- Diesel fuel sampling to analyze the fuel quality is recommended for anyone with fuel stored for longer than 6 months. This will help eliminate any surprises.
- If the fuel analysis from the laboratory shows too many contaminants, we recommend diesel fuel polishing services. Your fuel is cycled through a system to remove impurities. Fuel stabilizers can be added to fix certain issues. This can save a significant amount of money as compared to disposing of the old fuel, cleaning the tank, and replacing it with new fuel.
Generator Battery Failure
A dead or weak battery can prevent the generator from starting, rendering it useless during a power outage. Loose connections or corrosion on battery terminals can impede the flow of electrical current, leading to unreliable starts. Sulfation, the buildup of lead sulfate crystals, can occur if the battery remains discharged for extended periods, reducing its capacity and lifespan.
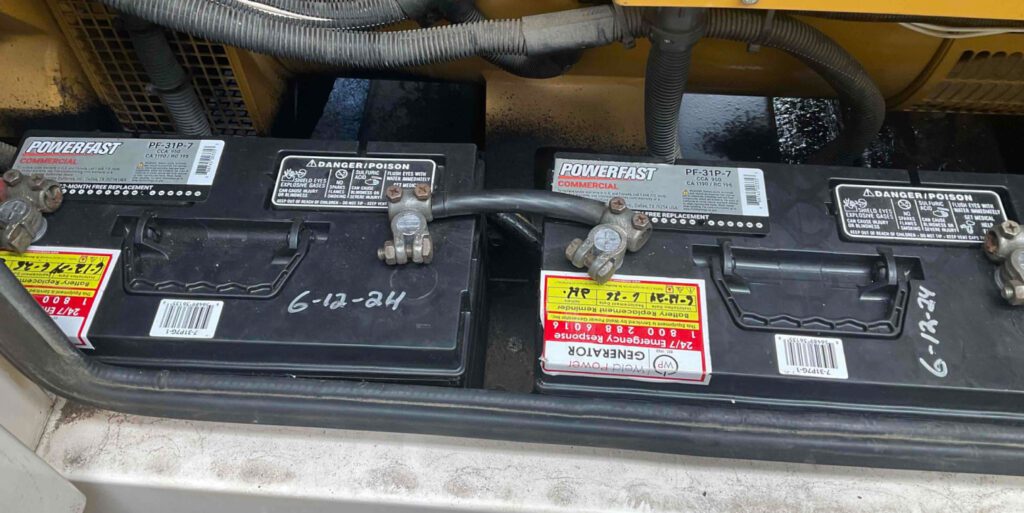

Additionally, a failing battery may not hold a charge or might drain quickly, causing intermittent operation. This is particularly problematic in standby generators, which rely on the battery to start automatically during an outage.
How to prevent generator battery failure?
- Regularly inspecting, cleaning, and testing the battery can prevent these issues. Ensuring tight connections and keeping terminals free from corrosion will help maintain their reliability. This should all be included in your generator maintenance plans.
- Weld Power Generator recommends replacing your generator batteries once every 3 years to help avoid any battery failures
Low Coolant / Antifreeze
Low coolant levels can lead to engine overheating, causing severe damage such as warped cylinders, cracked heads, or blown gaskets. This can result in costly repairs or total engine failure.
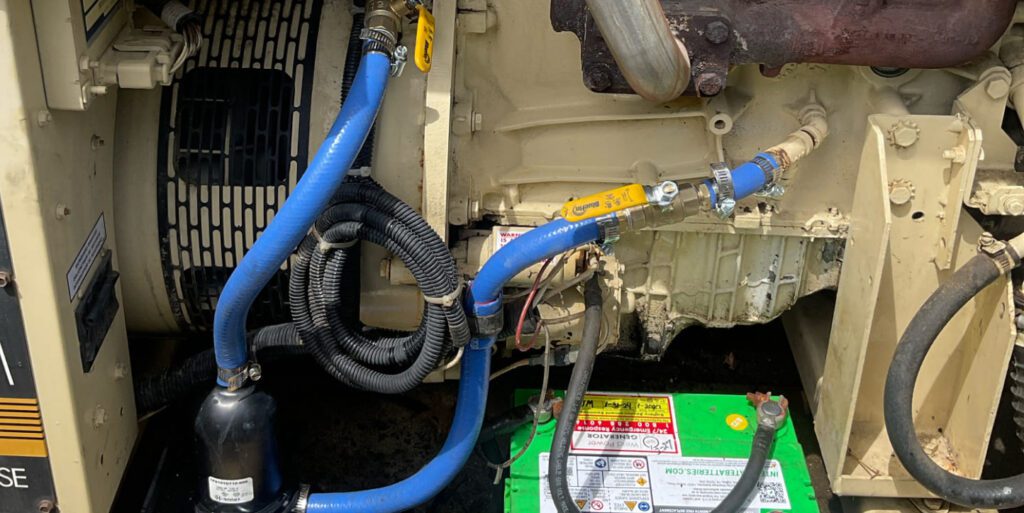

Overheating and low coolant levels can trigger automatic shutdowns, making the generator unavailable during critical power outages. Using the wrong type of coolant can result in inadequate protection against overheating, freezing, or corrosion. Some coolants may not be compatible with the generator’s materials, leading to internal corrosion, clogging, or degradation of seals and hoses. Contaminated coolant, containing debris or rust, can block the cooling passages, impeding proper heat dissipation and leading to overheating.
How to prevent low coolant/antifreeze in generators?
- Routine generator inspections include checking coolant levels and topping off as needed. As well as inspecting hoses for leaks.
- Ensure the coolant mixture is appropriate for the operating environment. Using manufacturer-recommended coolant types and mixtures ensures the generator runs smoothly and reliably, avoiding the risks associated with improper cooling system maintenance.
- Coolant sampling and laboratory analysis will indicate if there is inadequate protection. This can also help find internal issues with the generator before they become larger problems.
- Flushing and replacing the coolant at recommended intervals help prevent the buildup of contaminants and maintain optimal cooling efficiency.
Lubrication Issues
Contaminated oil, filled with dirt or metal particles, can cause blockages in the lubrication system, impeding the oil flow. Insufficient or degraded oil can lead to increased friction and wear on engine components. Both contaminated and degraded oil will exacerbate wear and tear on the generator. Without adequate lubrication, moving parts grind against each other which can result in overheating, potential engine seizure, or even complete engine failure. Additionally, low oil levels can trigger safety shutdown mechanisms, rendering the generator inoperable during crucial times.

How to prevent lubricant issues in generators?
- The generator should be examined regularly for any oil leaks, as well as checking the oil level.
- Oil sampling and lab analysis can help prevent any issues and warn you about any internal generator issues.
- Regular oil changes and oil filter replacement should be part of your preventative maintenance plan.
Lack of Generator Maintenance
Without regular generator maintenance, components like air filters, spark plugs, and belts can become dirty or worn out, leading to inefficient operation or complete engine failure. Accumulated debris and dust can clog cooling systems, causing the generator to overheat and potentially suffer severe engine damage.

How to easily set up scheduled generator maintenance?
- Make sure that the generator, especially the radiator and exhaust, is clear of any leaves or debris
- Air filters and belts should be changed on a regular basis
- Regular generator inspections and maintenance ensure that all parts are in good working condition, helping to catch and fix small problems before they become major issues, ensuring the generator operates reliably when needed most.
Rodent Damage
Rodents chew on wires and insulation, causing electrical short circuits and exposing live wires, which can lead to power system failures and even fire hazards.

Damaged wiring can disrupt the generator’s ability to start, stop, or run efficiently, resulting in operational inconsistencies or complete breakdowns. Rodents can also nest inside the generator’s housing, clogging air intake vents and obstructing proper ventilation.
This can cause the generator to overheat, leading to engine damage or failure. Nesting materials, such as leaves and debris, can further increase the risk of fire and reduce the efficiency of cooling systems. Additionally, rodents may gnaw on fuel lines, hoses, or belts which can disrupt the mechanical systems, leading to premature wear and the potential for critical failures during operation.
How to prevent rodent damage in generators?
- To prevent rodent damage, regularly inspect and clean the generator, ensuring no signs of infestation.
- Use rodent deterrents and seal any gaps or entry points around the generator housing. Maintaining a clean and rodent-free environment around your generator helps ensure its reliability and longevity, especially during critical power needs.
Wet Stacking
Wet stacking is a common issue in diesel generators that occurs when the engine operates under a light load for extended periods. This condition results in unburned fuel accumulating in the exhaust system, leading to a range of problems. Key symptoms include black smoke, excessive soot buildup, and oily residue leaking from the exhaust.

Over time, wet stacking can foul injectors, reduce combustion efficiency, and cause carbon buildup on the exhaust valves, turbocharger, and other critical components. This buildup impairs the generator’s performance, leading to reduced power output, increased fuel consumption, and higher emissions. If left unaddressed, it can cause significant engine damage and shorten the generator’s lifespan.
How to prevent wet stacking?
- To prevent wet stacking, the generator must be operated at or near its optimal load capacity regularly. This practice ensures complete fuel combustion and prevents the accumulation of unburned fuel.
- Periodically performing a load bank test, which involves running the generator at a higher load under controlled conditions, can also help burn off excess fuel and clean the exhaust system.
Control Panel Issues
The control panel is the generator’s command center, managing operations such as starting, stopping, and monitoring performance. Faulty control panels can prevent the generator from starting, rendering it useless during a power outage. Malfunctioning generator control panels may fail to regulate voltage and frequency properly, leading to unstable power output that can damage connected equipment and the generator itself. A defective control panel can also impair the generator’s ability to detect and respond to faults.

For instance, it might not shut down the generator during overheating or low oil pressure, causing severe engine damage. Additionally, inaccurate readings from the control panel can misdiagnose issues, resulting in ineffective or unnecessary repairs. Control panels with software issues or outdated firmware can experience glitches, causing intermittent operation or complete failure. Loose connections, corrosion, or water ingress can further compromise control panel functionality, leading to erratic behavior or short circuits.
How to prevent control panel issues on a generator?
- Regularly inspecting and testing the control panel, ensuring firmware is up to date, and addressing any signs of damage or wear can prevent these problems. Proper maintenance of the control panel ensures the generator operates reliably and efficiently, providing consistent power when needed most.
Overloading
Running a generator beyond its rated capacity leads to excessive heat buildup, which can damage internal components such as the engine, alternator, and wiring. Overheating can result in melted insulation, burned-out circuits, and potential fire hazards. Additionally, overloading can cause the generator to trip its circuit breaker or blow a fuse, leading to sudden power loss.

Frequent tripping can wear out these protective components, making them less effective. The strain of handling too much load can also result in inefficient operation, with voltage fluctuations that can damage sensitive electronic equipment connected to the generator. Overloading can lead to reduced fuel efficiency, as the generator works harder to meet the excessive demand, consuming more fuel and increasing operating costs. Persistent overloading stresses the engine, causing accelerated wear and tear, potentially leading to costly repairs and a shortened lifespan for the generator.
How to prevent generator overloading?
- To prevent these problems, it’s crucial to understand your generator’s capacity and avoid exceeding it. Implementing load management strategies, such as staggering the start of large appliances, can help balance the load and ensure the generator operates within safe limits.
- Regularly monitoring the generator also helps detect and address potential overloading issues early.
Improper Installation
Improper installation can lead to numerous generator problems, compromising its reliability and safety. Incorrect electrical connections can result in poor voltage regulation, causing power surges or insufficient power delivery, which can damage connected appliances and the generator itself. Poor ventilation or inadequate placement can cause overheating, as generators need proper airflow to dissipate heat effectively.

Overheating can lead to engine damage and reduce the generator’s lifespan. Improper installation can also result in excessive vibration and noise, leading to structural damage and loosening of internal components over time. Incorrect alignment or securing of the generator can cause wear and tear on parts, leading to frequent breakdowns and increased maintenance costs. Additionally, an inadequately installed generator may not activate during a power outage, defeating its primary purpose.
How to install a generator correctly?
- To avoid these issues, hire a qualified generator company for installation, ensure compliance with all regulations, and follow the manufacturer’s instructions closely. Weld Power offers turnkey generator installations and ATS sales for all commercial needs.
Conclusion
Generators are a critical component in ensuring uninterrupted power supply, especially in emergencies. A multipoint generator preventative maintenance program is the key to preventing most failures. Contact us for a free quote. By understanding and mitigating these common failure causes, you can ensure your generator remains reliable and ready to perform when needed.
